Which Zeros Matter? : 4.25
Supporting materials
- Related Progression Points
- Developmental Overview of Numeration: Base Ten and Place Value Properties (PDF - 28Kb)
Indicator of Progress
Students are able to explain the value of any decimal number in terms of place value, and can convert between tenths, hundredths etc.
One of the final steps is to be able to deal with zero confidently in any position.
Zero is tricky in both its roles: as a digit, and as a number. The basic rule is that a zero affects the size of a number if it is placed between the ones column and non-zero digits. In the number 00.070, only the underlined zero (between the 7 and the ones column) affects its size. The other zeros do not. In the whole number 00120300, only the underlined zeros (between the 1, 2 or 3 and the ones column) affects its size. The other zeros do not.
Illustration 1
Indicators that more attention to the significance of zero is required include:
(i) thinking that 3.720 is greater than 3.72
(ii) overgeneralisation of the 'append a zero' rule when multiplying by 10
e.g. from the correct 153 × 10 = 1530 to the incorrect 1.53 × 10 = 1.530
(iii) overgeneralising from the correct 4.860 = 4.86 to the incorrect 4.086 = 4.86
(iv) with whole numbers, being unclear that 32 = 032 = 0032
Teaching Strategies
The teaching strategy here is to prompt students to clarify the roles of zero, by providing unusual examples which provoke cognitive conflict, resolved by class and group discussion.
Activity 1: Digits vs numbers clarifies the distinction between what is a digit and what is a number.
Activity 2: Funny Numbers provides opportunities, in the form of a game, for group and class discussion about the relative size of decimal numbers that have zeros in unusual positions.
Activity 3: Number Slides uses visual aids to raise and answer questions of which place value columns need to be filled by zeros.
Activity 1: Digits vs numbers
Improve classroom communication by making sure students distinguish between the terms 'digit' and 'number'. Everyone would agree that it is important that students appreciate the difference between a 'letter' and a 'word' yet many students do not appreciate this important distinction between 'digit' and 'number'. A digit is like a letter and a number (or numeral) is like the whole word. Just as the word 'cat' has three letters, the number 845 has three digits, 8, 4 and 5 when written in our base ten system.
Activity 2: Funny Numbers
The game of Funny Numbers provides opportunities for group and class discussion about the relative size of decimal numbers. The set of cards includes many zeros.
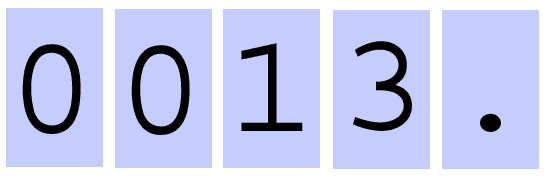
Activity 3: Number Slides
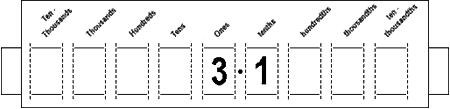
Use Number Slides to show multiplication and division by powers of ten. This requires a good understanding of which place value columns need to be filled by zeros.
References
These activities are published with permission from Steinle, V., Stacey, K. & Chambers, D. (2006) Teaching and Learning about Decimals. (Version 3.1 ) Faculty of Education, University of Melbourne . (CD-ROM).
